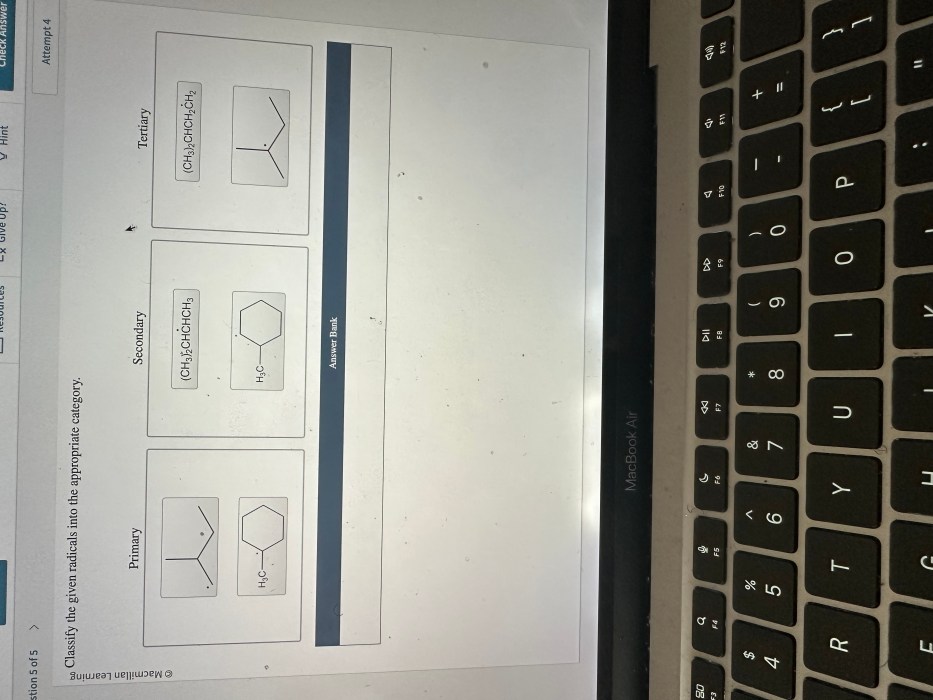
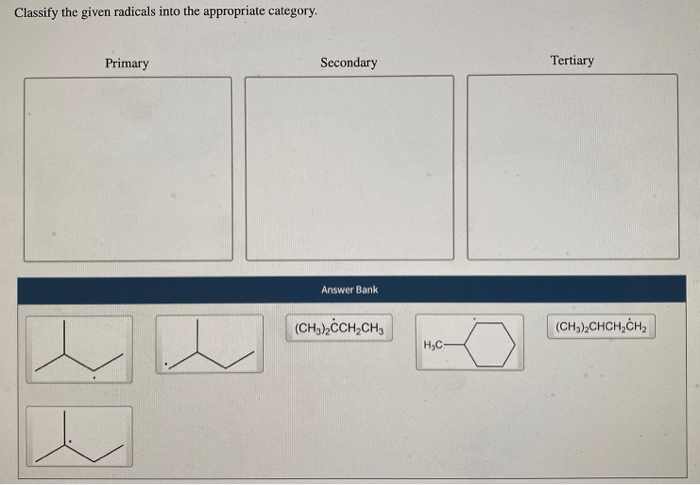
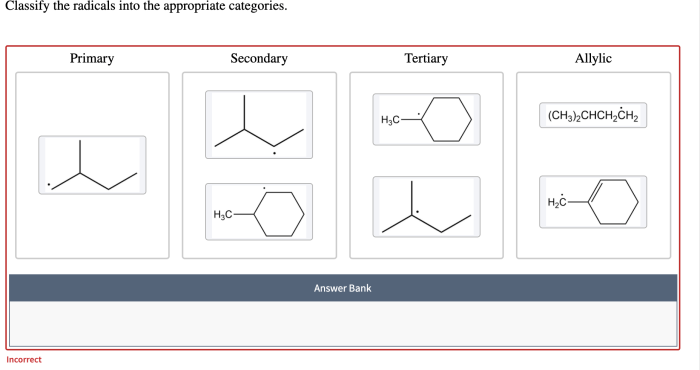
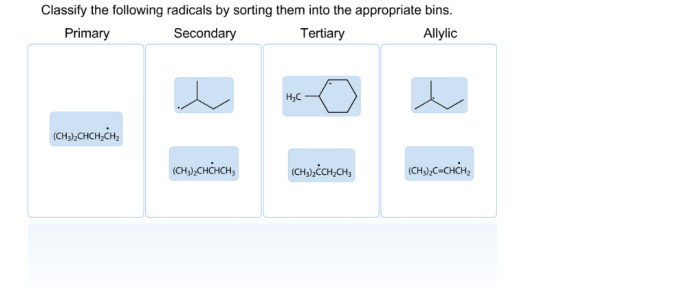
Classify the given radicals into the appropriate category. Radicals are highly reactive chemical species with unpaired electrons, making them crucial for various chemical reactions and processes. Classifying radicals helps us understand their behavior, properties, and reactivity. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of radical classification, including types, criteria, methods, applications, challenges, and limitations.
The study of radicals has significant implications in diverse fields such as organic chemistry, biochemistry, and environmental science. By understanding the classification of radicals, scientists can gain insights into their role in various chemical and biological systems.
Classification of Radicals
Radicals are chemical species that contain one or more unpaired electrons. They are highly reactive and can participate in a variety of chemical reactions.
Classifying radicals is important for understanding their reactivity and behavior. It helps us to identify different types of radicals, their properties, and their potential applications.
Types of Radicals
- Carbon-centered radicals:These radicals have an unpaired electron on a carbon atom.
- Nitrogen-centered radicals:These radicals have an unpaired electron on a nitrogen atom.
- Oxygen-centered radicals:These radicals have an unpaired electron on an oxygen atom.
- Halogen-centered radicals:These radicals have an unpaired electron on a halogen atom.
- Metal-centered radicals:These radicals have an unpaired electron on a metal atom.
Criteria for Classification
Radicals can be classified based on a number of criteria, including:
- The type of atom that bears the unpaired electron
- The number of unpaired electrons
- The stability of the radical
- The reactivity of the radical
Methods of Classification
There are a number of different methods that can be used to classify radicals. One common method is to use the IUPAC system, which is based on the type of atom that bears the unpaired electron.
Another method of classification is to use the number of unpaired electrons. Radicals can be classified as either free radicals or trapped radicals. Free radicals have one or more unpaired electrons, while trapped radicals have their unpaired electrons localized on a specific atom or molecule.
Applications of Radical Classification
Classifying radicals is important for a number of reasons. It helps us to understand the reactivity and behavior of radicals, and it can also help us to design new drugs and materials.
For example, classifying radicals can help us to understand the role that they play in cancer. Radicals are known to be involved in the formation of tumors, and they can also contribute to the development of cancer metastasis.
Challenges and Limitations
There are a number of challenges associated with classifying radicals. One challenge is that radicals are often unstable and difficult to study. Another challenge is that there is no single classification system that is universally accepted.
Despite these challenges, classifying radicals is an important area of research. By understanding the different types of radicals and their properties, we can better understand the role that they play in a variety of chemical reactions.
Question & Answer Hub: Classify The Given Radicals Into The Appropriate Category.
What are the key characteristics used to classify radicals?
Key characteristics include the number of unpaired electrons, the type of atom or group bearing the unpaired electron, and the stability of the radical.
What are the practical applications of classifying radicals?
Classifying radicals aids in understanding their role in combustion, polymerization, and biological processes. It also helps in designing new drugs and materials.
What are the challenges in classifying radicals?
Challenges include the high reactivity of radicals, making them difficult to isolate and study. Additionally, the stability and behavior of radicals can vary depending on the environment.