Ciudad boliviana ubicada a los pies del cerro rico – Nestled at the foot of the towering Cerro Rico, the Bolivian city of Potosí stands as a testament to the rich history, cultural heritage, and socioeconomic significance of this iconic mountain. From its role as a major silver mining center to its status as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, the city’s development has been inextricably intertwined with the Cerro Rico, shaping its identity and leaving an enduring legacy.
The Cerro Rico has played a pivotal role in Potosí’s historical significance, serving as the source of vast silver deposits that fueled the Spanish Empire’s economy. Mining activities have left an indelible mark on the city’s landscape and culture, with numerous historical landmarks and cultural heritage sites dotting the area.
Historical Significance of the Cerro Rico: Ciudad Boliviana Ubicada A Los Pies Del Cerro Rico
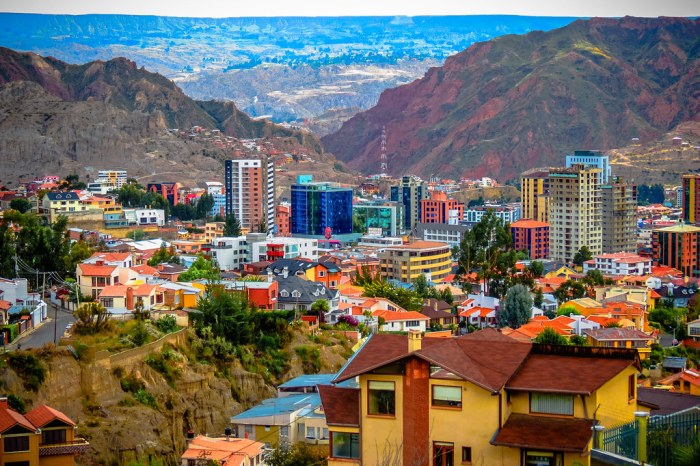

The Cerro Rico, also known as the Rich Mountain, is a towering mountain located in the heart of Potosí, Bolivia. Its historical significance is deeply intertwined with the development of the city and the region. The mountain’s vast silver deposits have played a pivotal role in shaping the economic, social, and cultural landscape of Potosí and Bolivia.
Mining activities began in the Cerro Rico in the 16th century, and the mountain quickly became one of the most important silver mines in the world. The influx of wealth and labor transformed Potosí into a thriving metropolis, attracting people from all corners of the Spanish Empire.
The silver from the Cerro Rico financed the Spanish crown’s military campaigns and fueled the development of European economies.
Role of Mining in the City’s History and Economy
- Mining in the Cerro Rico was a major source of wealth for the Spanish crown and the city of Potosí.
- The silver from the mine financed the Spanish military campaigns and fueled the development of European economies.
- Mining activities led to the establishment of a large workforce and the growth of Potosí’s population.
- The wealth generated from mining contributed to the development of infrastructure, art, and architecture in the city.
Historical Events and Figures Associated with the Cerro Rico, Ciudad boliviana ubicada a los pies del cerro rico
The Cerro Rico has witnessed numerous historical events and is associated with several prominent figures:
- The siege of Potosí in 1810, during the Bolivian War of Independence, was a key battle in the struggle for independence from Spain.
- Simón Bolívar, the liberator of South America, visited Potosí in 1825 and was presented with a silver crown made from the Cerro Rico’s silver.
- The mountain has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1987, recognizing its historical and cultural significance.
FAQ Section
What is the historical significance of the Cerro Rico?
The Cerro Rico was a major source of silver for the Spanish Empire, making Potosí one of the wealthiest cities in the world during the 16th and 17th centuries.
What are some of the cultural heritage sites located near the Cerro Rico?
The city of Potosí is home to numerous cultural heritage sites, including the Casa de la Moneda (Mint), the Convent of Santa Teresa, and the Church of San Lorenzo.
What is the socioeconomic impact of the Cerro Rico?
Mining activities at the Cerro Rico have had a significant socioeconomic impact on Potosí, providing economic benefits but also posing challenges related to environmental degradation and social issues.